Wholesale Spiral Wound Gasket Just in One Place
- The Ultimate Solutions
Want to wholesale Sealing Gaskets in China? This ultimate solution guide would help you everything about wholesaling Spiral Wound Gasket.

Hi, I'm John from GASKETOO. Let me guide you through this ultimate solutions page.
I have been working with GASKETOO for 12 years now. Click the button below to get great ideas on how we provide you with exceptional solutions for Spiral Wound Gasket and other gasket products.

All you need to know about Spiral wound gasket
Table of Contents
- What is Spiral Wound Gasket?
- Spiral Wound Gasket: Components & Mechanism
- Spiral Wound Gasket Types
- Spiral Wound Gasket Color Code Chart
- Spiral Wound Gasket Dimensions Chart & Customized
- What's the Use of Spiral Wound Gasket?
- Advantages of Spiral Wound Gasket?
- Manufacturing process of Spiral Wound Gasket
- Spiral Wound Gasket VS Flat Gasket

Download this page as a PDF
To save you time, we have also prepared a PDF version containing all the contents of this page, only leave your email and you will get the download link immediately.
What is Spiral Wound Gasket?
A Spiral Wound Gasket is a type of mechanical sealing device that is commonly used in piping and pressure vessel applications to prevent the leakage of liquids or gases.
It consists of a metallic strip (typically stainless steel) wound in a spiral fashion around a soft filler material, such as graphite or PTFE. The combination of the metal strip and the filler material provides both a physical barrier and a compression seal to prevent leaks.
- Spiral Wound Gaskets are known for their reliability and versatility, and are used in a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation.
- They are also able to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for use in harsh and demanding environments.

Spiral Wound Gasket: Components & Mechanism

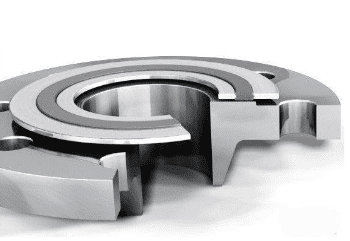
The components of a Spiral Wound Gasket include:
- Inner Ring or Centering Ring: This is a circular ring that provides a center for winding the gasket and helps to maintain the concentricity of the gasket.
- Winding Strip: This is the main body of the gasket and is made of a metallic strip (usually stainless steel) that is wound in a helical pattern around the inner ring. The winding strip provides the main sealing element and helps to distribute the pressure evenly around the gasket.
- Filler Material: This is a compressible material that is placed between the winding strip and the flange faces. The filler material helps to reduce the stress on the winding strip and provides a secondary sealing element. The filler material can be made of various materials such as graphite, PTFE, asbestos, or ceramic.
- Outer Ring or Casing: This is a circular ring that helps to maintain the shape of the gasket and provides a surface for clamping the gasket to the flange faces.
The mechanism of a Spiral Wound Gasket is as follows:
- When the flange bolts are tightened, the gasket is compressed between the flange faces, causing the filler material to deform and fill any imperfections in the flange faces.
- The winding strip is then subjected to radial compression, which results in a small amount of radial deformation. This deformation causes the winding strip to generate a sealing force that helps to prevent any leakages around the gasket.
- The radial compression of the winding strip also results in an axial compression that helps to maintain the concentricity of the gasket and provide additional sealing force.
Overall, the combination of radial and axial compression of the winding strip, along with the deformation of the filler material, provides an effective seal that helps to prevent leakages in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Spiral Wound Gasket Types By Design


Standard Type
Gasket Thickness: 4.5mm, 3.2mm
Stainless steel tube material
Application: Flat flange


With outer guide ring and inner ring attached
Outer/inner ring: Low Carbon Steel 3.2mm
Stainless Steel 3.0mm
Gasket Thickness: 4.5mm
Application: Smooth butt-welding flange


With outer guide ring attached
Outer/inner ring: Low Carbon Steel 3.2mm
Stainless Steel 3.0mm
Gasket Thickness: 4.5mm
Application: Smooth flat slide flange


With inner ring attached
Outer/inner ring: Low Carbon Steel 3.2mm
Stainless Steel 3.0mm
Gasket Thickness: 4.5mm
Application: Embedded female and male flange
Spiral Wound Gasket : Color Code Chart &
Temperature Limits

Spiral Wound Gasket Dimensions Chart & Customized


Custom Gaskets
Spiral wound gaskets can be made to meet any size specifications. Options for design include multiple winding layers and rings, which can be combined with a variety of fillers or unique winding materials and ring shapes. Simply describe your application or send us a drawing and we will assist you in designing the best fit for your needs.
What's the Use of Spiral Wound Gasket
Spiral wound gaskets are commonly used in a variety of applications where a tight seal is required to prevent leakage of liquids or gases. They are often used in piping systems in various industries such as petrochemical, power generation, pharmaceuticals, and others. Some specific applications for spiral wound gaskets include:
-
Flanges: Spiral wound gaskets are used to provide a tight seal between two flanges in a piping system.
-
Pressure vessels: They are used to prevent leakage in pressure vessels and storage tanks.
-
Heat exchangers: They are used in heat exchanger systems to prevent the leakage of fluids between two sections.
-
Valves: Spiral wound gaskets are also used in valves to prevent the leakage of fluids or gases.
Spiral wound gaskets are preferred for their reliability, durability, and ease of installation. They can be designed to handle high temperature and pressure applications and are versatile enough to be used in a variety of different industries and applications.
Advantages of Spiral Wound Gasket?
Why choose Spiral Wound Gaskets?
High temperature and pressure resistance
Versatility
Easy installation
Durability
Cost-effective
Improved sealability
Manufacturing process of Spiral Wound Gasket
The manufacturing process for spiral wound gaskets involves several steps:

STEP 1
Cutting the V-shaped metallic winding strip:
The first step is to cut the V-shaped metallic winding strip from a coil of metal, typically stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloy. This strip forms the basic structure of the gasket.

STEP 2
Measuring and cutting the filler material:
The next step is to measure and cut the filler material, which is usually made of graphite, ceramic, or PTFE (Teflon). This filler material provides a soft, flexible seal against the flanges and compensates for any irregularities or fluctuations in pressure.

STEP 3
Assembling the gasket:
The metallic winding strip and filler material are then placed in a jig and wound together in a spiral pattern, with the metallic strip on the outside and the filler material on the inside. The winding is done under tension to ensure a tight seal and prevent any leaks.

STEP 4
Trimming the gasket:
After the gasket has been wound, it is trimmed to the desired size, taking into account the size and shape of the flanges it will be used with.

STEP 5
Inspecting the gasket:
Finally, the gasket is inspected for defects and its overall quality is checked to ensure that it meets the necessary standards and specificati

STEP 6
Packing:
Arrange your shipments with the best rates and carriers to ensure they get where you want them when needed!
Spiral Wound Gasket VS Flat Gasket
Spiral Wound Gaskets and Flat Gaskets are both commonly used in industrial applications, but they have some differences in terms of their features and benefits.
Advantages of Spiral Wound Gaskets:
- Can handle high temperatures and pressures
- Have a longer lifespan compared to flat gaskets
- Offer a tight and leak-proof seal
- Are versatile and can be used with different flange materials and in various industries
- Are easy to install and do not require special tools
Advantages of Flat Gaskets:
- Are more cost-effective compared to Spiral Wound Gaskets
- Have a simple design and are easier to manufacture
- Are commonly used in low-pressure and low-temperature applications
- Are easily cut and customized to fit specific applications
In conclusion, both Spiral Wound Gaskets and Flat Gaskets have their own unique advantages, and the choice between them will depend on the specific requirements of the application, such as temperature, pressure, and chemical resistance. Spiral Wound Gaskets are typically used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, while Flat Gaskets are commonly used in low-pressure and low-temperature applications.
Request A Free Quote
We'd like to work with you
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. Our experts will give you a reply within 24 hours.
- +86 577 8693 2718
- +86 130 5776 5697
- [email protected]

